GoMLC
|
4.1 - Neuromuscular Function
4.1.1 Label a diagram of a motor unit
4.1.2 Explain the role of neurotransmitters in stimulating skeletal muscle contraction. 4.1.3 Explain how skeletal muscle contracts by the sliding filament theory. 4.1.4 Explain how slow and fast twitch fiber types differ in structure and function. |
4.1 Support
Motor units and Neurons - read more. http://www.teachpe.com/anatomy/nerves.php
4.1 Files
| ||||||
Why do we learn about neurotransmitters and muscle contraction?
- Alzhiemer's and Acetylcholine - "Doctors are now willfully poisoning acetylcholinesterase in an attempt to reverse the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. People with Alzheimer's disease lose many nerve cells as the disease progresses. By taking a drug that partially blocks acetylcholinesterase, the levels of the neurotransmitter can be raised, strengthening the nerve signals that remain." - http://pdb101.rcsb.org/motm/54
- Botox and Acetylcholine - http://dermatology.about.com/od/cosmeticprocedure/a/botox.htm_
- Alzhiemer's and Acetylcholine - "Doctors are now willfully poisoning acetylcholinesterase in an attempt to reverse the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. People with Alzheimer's disease lose many nerve cells as the disease progresses. By taking a drug that partially blocks acetylcholinesterase, the levels of the neurotransmitter can be raised, strengthening the nerve signals that remain." - http://pdb101.rcsb.org/motm/54
- Botox and Acetylcholine - http://dermatology.about.com/od/cosmeticprocedure/a/botox.htm_
4.1.3 Sliding Filament Theory
|
|
|
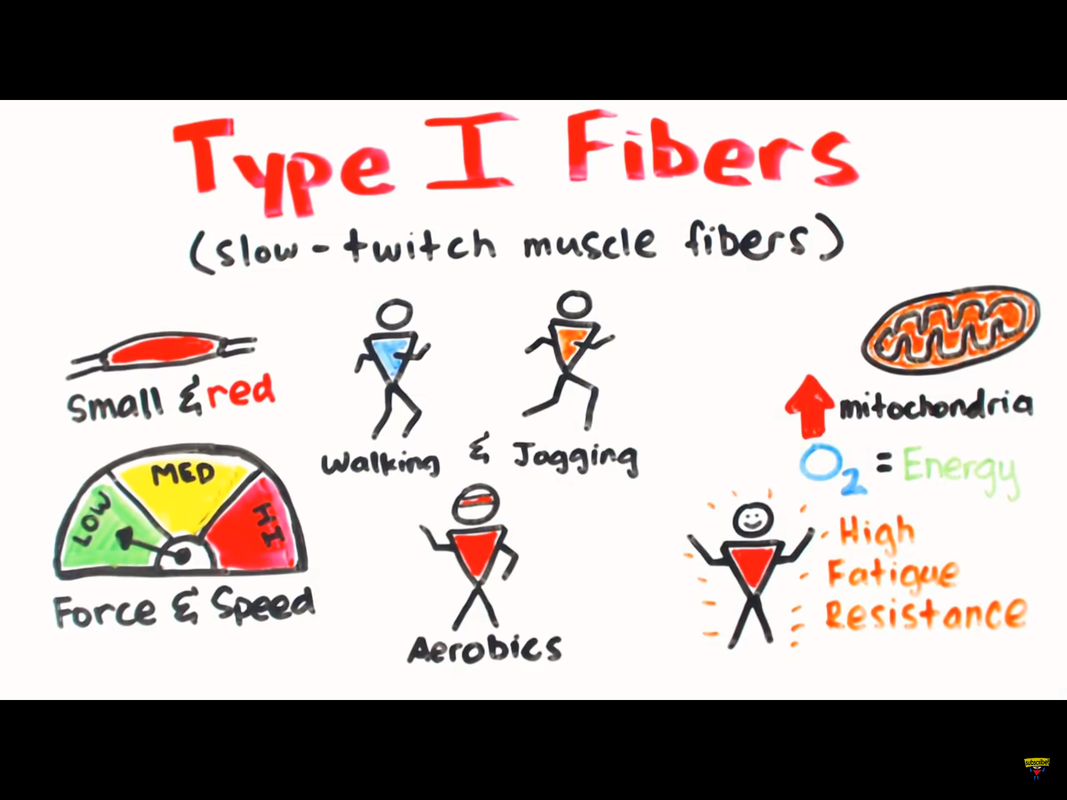
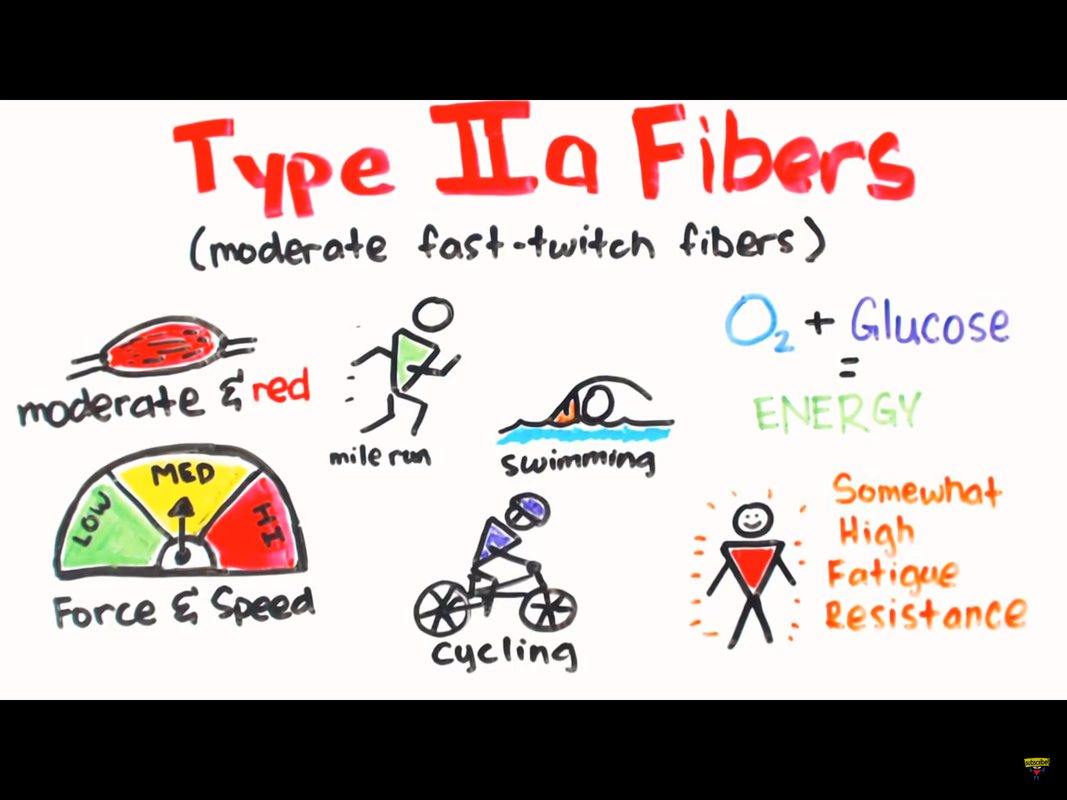
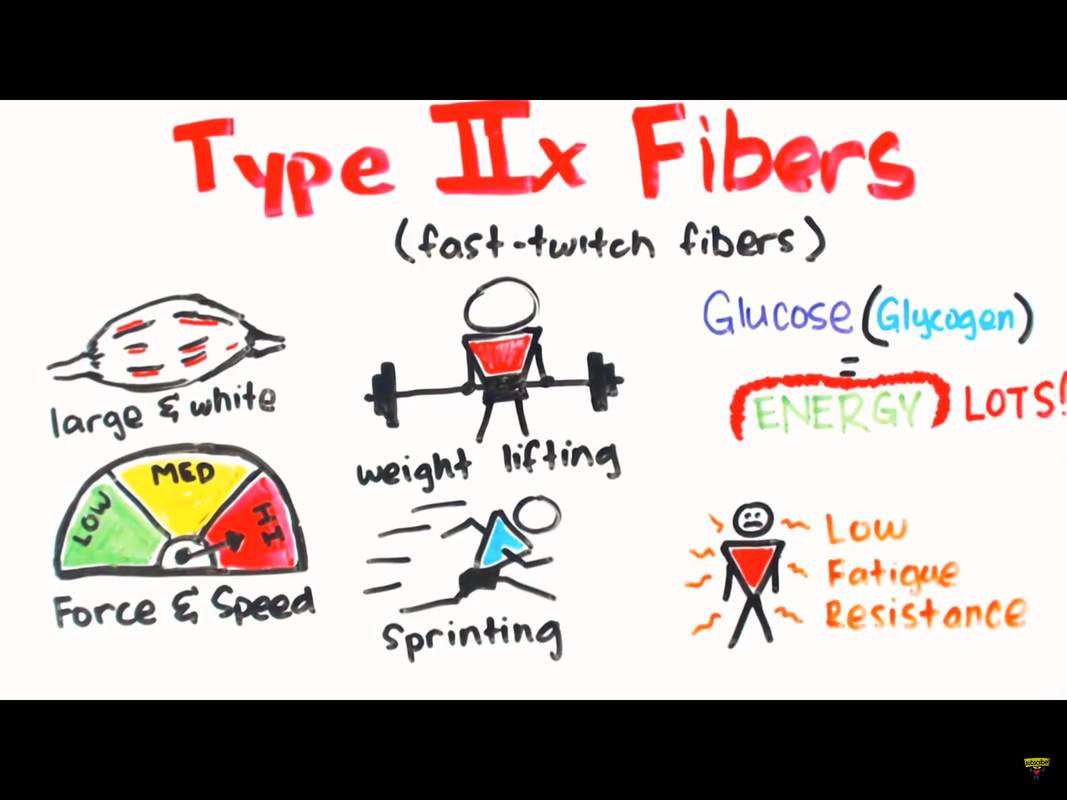
4.1.4 Muscle Fiber Types
|
|
|
4.2 Joint and Movement Type
|
4.2.1 - Outline the types of movement of synovial joints.
4.2.2 - Outline the types of muscle contraction. 4.2.3 - Explain the concept of reciprocal inhibition. 4.2.4 - Analyze movements in relation to joint action and muscle contraction. 4.2.5 - Explain delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS) in relation to eccentric and concentric muscle contractions. |
4.2 Support
Planes of Motion - Visit the American Council on Exercise (ACE) to learn more
Planes and Anatomy Basics - The website teachpe.com supports the UK version of SEHS and the IB (great stuff) Topic 4.2.3 - 4.2.5 PREZI - Check out another presentation of the material covered in these assessment statements!4.2 Files |
|
|
|
|
|
|
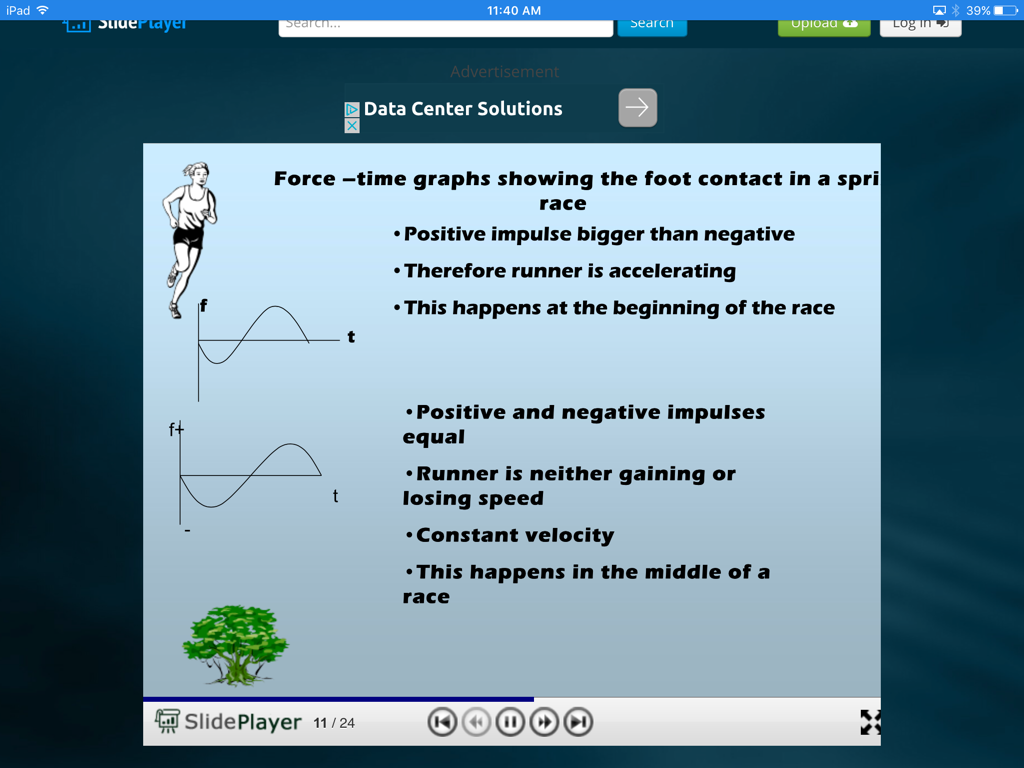
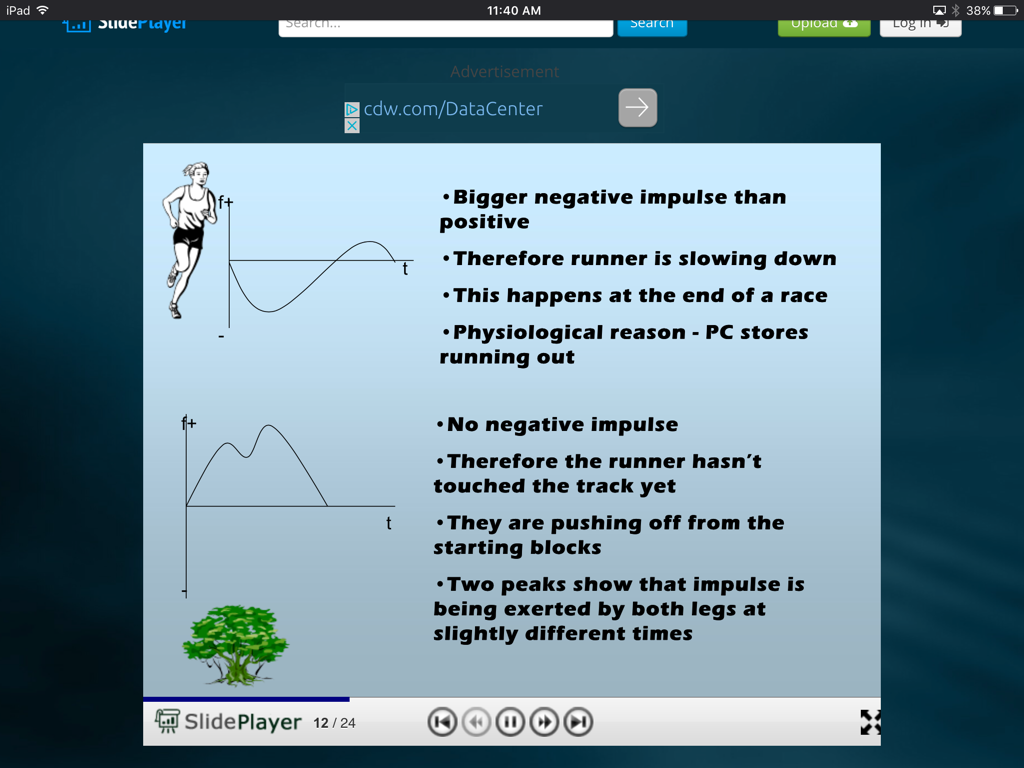
Topic 4.3 - Biomechanics
Article from the American Sports College of Medicine on DOMS - check it out! https://www.acsm.org/docs/brochures/delayed-onset-muscle-soreness-(doms).pdf
|
|
|
Read about Lactic Acid! http://www.brianmac.co.uk/lactic.htm_ This is a longer read with biological processes included!
Excellent read about who is the real MVP in the lactic acid debate. http://www.details.com/story/lactic-acid-workout
Excellent read about who is the real MVP in the lactic acid debate. http://www.details.com/story/lactic-acid-workout
Web Links - 4.3 Biomechanics
NEED TO UPDATE
|
|
|
Analyzing Graphs - this is a UK site tied to their version of the SEHS class :)
Newtons Laws explained
|
|
|
|
|
Angular Momentum
|
|
|
|
|